BioPose: Advancing Biomechanically-Accurate 3D Pose Estimation – Accepted at WACV 2025
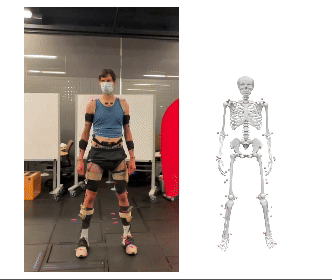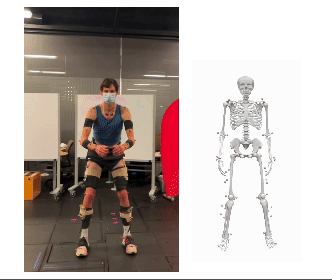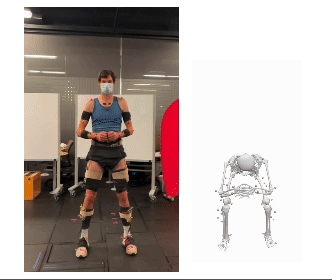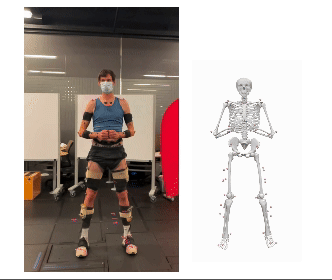
We are pleased to announce that our paper, “BioPose: Biomechanically-Accurate 3D Pose Estimation from Monocular Videos,” has been accepted for presentation at WACV 2025. This work introduces a novel framework for biomechanically accurate 3D human pose estimation, bridging the gap between learning-based methods and physics-based motion analysis.
Advancing 3D Pose Estimation for Real-World Applications
Conventional 3D pose estimation methods struggle with biomechanical plausibility, limiting their applications in biomechanics, healthcare, rehabilitation, and robotics. While marker-based motion capture systems provide high accuracy, they are often costly and impractical for many real-world scenarios. BioPose addresses this challenge by introducing a learning-based framework that ensures biomechanical feasibility while achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance.
Key Contributions of BioPose:
- Multi-Query Human Mesh Recovery (MQ-HMR): A novel multi-scale deformable transformer that enhances the accuracy of 3D human mesh reconstruction.
- 2D-Informed Pose Refinement: Aligns 3D pose estimates with 2D cues, ensuring improved consistency and anatomical accuracy.
- Neural Inverse Kinematics (NeurIK): A spatial-temporal network that leverages mesh vertices as virtual markers, applying biomechanics-guided constraints to refine human joint movements.
This research presents a significant step forward in AI-driven human motion analysis, with potential applications in clinical motion assessment, sports science, and human-computer interaction.
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to the research team, Muhammad Usama Saleem, Farnoosh Koleini, Pu Wang, Hongfei Xue, Ahmed Helmy, and Abbey Fenwick, for their contributions to this work.
Read more about BioPose: Publication Link
Stay connected for more updates on AI-driven biomechanics and healthcare innovations.